The First-Ever Human-to-Human Dream Communication Did It Really Happen?
A neurotech company claims two people exchanged messages in a dream—science or speculation?

Dreams have fascinated humans for centuries. From ancient prophecies to modern neuroscience, our subconscious world has remained an enigma.
The idea of two people connecting within a dream has long been a fantasy explored in myths and science fiction. But now, a California-based neurotech company, REMspace, claims to have made it a reality.
According to their experiment, two individuals successfully exchanged a message—not through speech or text, but entirely within a lucid dream.
If true, this could revolutionize our understanding of consciousness, human connection, and even the limits of communication itself.
But is this breakthrough real, or is it another bold claim awaiting scientific validation? While REMspace celebrates it as a historic milestone, many experts remain skeptical.
Until independent verification confirms their results, the world is left wondering—have we unlocked a new frontier of human interaction, or is this just another dream waiting to be debunked?

The Science of Dreams and Lucid Dreaming
Dreams are often thought of as a gateway to the subconscious, but scientifically, they are complex neurological events.
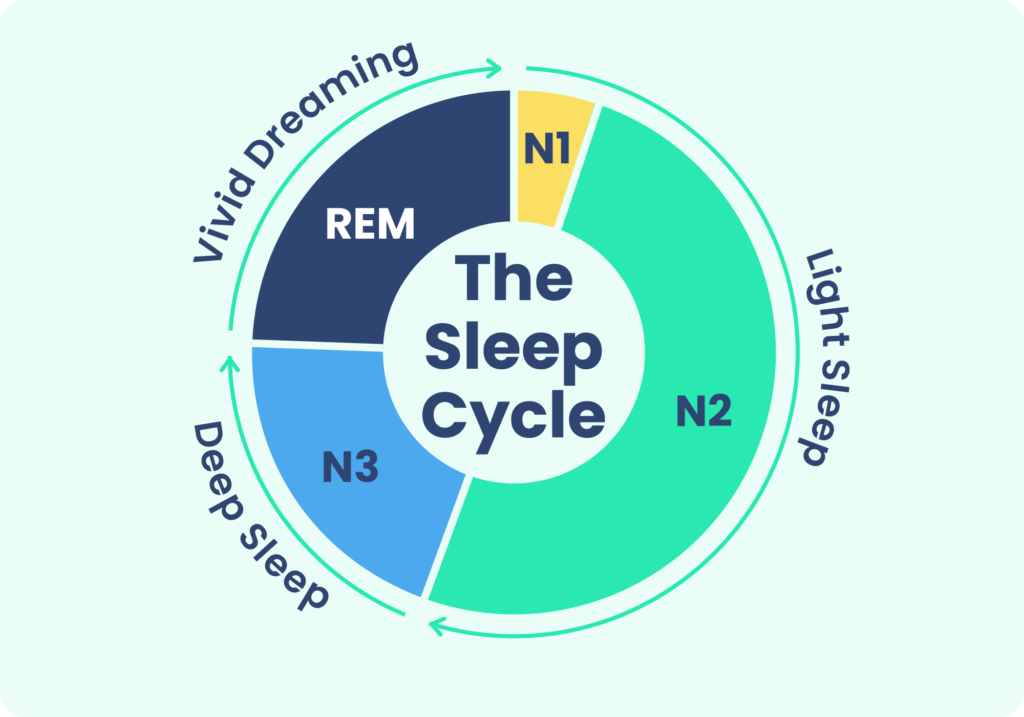
They occur primarily during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, where brain activity is heightened, similar to wakefulness.
During REM sleep, the brain generates vivid and immersive dream experiences, yet the body remains in a state of paralysis.

Lucid dreaming where a person becomes aware they are dreaming has been studied extensively. Some individuals can even control aspects of their dream environment.
Research has shown that external stimuli, such as flashing lights or audio cues, can influence dream content.
A 2021 study in Current Biology demonstrated that lucid dreamers could answer simple math problems presented through auditory cues while asleep.

These findings suggest that outside information can be processed in dreams—but communicating from one dreamer to another is an entirely different challenge.
Unlike a phone call or brain-computer interface, the human mind lacks a natural mechanism for transmitting thoughts between sleeping individuals.
For REMspace’s claim to hold up, their methods must be examined—and proven to work under controlled conditions.
The REMspace Experiment: A Closer Look
REMspace specializes in lucid dreaming research, and they claim to have recorded the first-ever dream-based human communication.
Their experiment involved two experienced lucid dreamers, each sleeping in separate locations, yet allegedly exchanging a message within their dreams.

How the Experiment Worked
Lucid Dream Induction – Both participants were trained to enter a lucid dreaming state.
Sleep Monitoring – Brain waves, heart rate, and breathing were tracked using polysomnographic equipment.
Message Transmission – The first participant, once lucid, received an audio cue containing a randomly generated word.
Dream Reception – Minutes later, the second participant reportedly “received” the word within their dream and repeated it after waking up.
The company claims this proves that human minds can communicate while asleep, bypassing traditional forms of messaging.
However, REMspace has not disclosed the specific word used, nor the precise mechanism by which the message was received in the dream state.
This lack of transparency raises significant concerns within the scientific community.
Without independent replication, skepticism remains high. Could it be suggestion, coincidence, or even flawed methodology?
For now, the experiment remains an intriguing claim—but far from confirmed science.

Why Scientists Are Skeptical
Groundbreaking discoveries require rigorous proof. So far, no independent researchers have replicated REMspace’s findings.
Until another team verifies the results under strict conditions, dream communication remains an unproven theory.

Could Dream Communication Ever Become Reality?
If REMspace’s claims withstand scientific scrutiny, the possibilities are enormous.
1. A New Era of Long-Distance Communication?
Imagine being able to hold conversations with someone across the world—without a phone, internet, or any external device.
If thoughts could be exchanged in real-time during dreams, communication as we know it could change forever.
2. Therapeutic Applications
Dream communication could offer breakthroughs in therapy, allowing patients to process emotions or trauma through guided dream interactions.
It could also be used to strengthen memory retention, problem-solving, or even skill development during sleep.
3. The Technology Challenge
For any of this to happen, more advanced technology is needed. EEG readings alone are not enough we would need precise tools to track and decode dream-based messages.
Until then, dream communication remains more of a scientific curiosity than a practical tool.

Davy